Core Concepts
Numia indexes transactional data and the events generated from each transaction, providing a robust dataset for analyzing blockchain activity. While we currently do not index state data directly, we are working on streaming state changes over time. In the meantime, you can reconstruct specific states by summing up transactions, as their events represent the deltas in state changes.
To effectively use Numia’s datasets, it’s essential to understand some key concepts of the Cosmos SDK presented in the following sections.
Blocks
Blocks are the fundamental units of the Cosmos blockchain, securing and organizing data. Cosmos chains use the CometBFT (formerly Tendermint BFT) consensus algorithm to validate transactions, secure the network, and commit blocks. Each block contains a set of transactions and serves as the highest-level object in Numia’s dataset.
Transactions
Transactions are signed user instructions that initiate state changes on the blockchain, such as sending tokens or interacting with applications. Before execution, transactions must be:
- Signed using the sender's private key.
- Broadcasted to the network.
- Included in a block and validated through consensus.
Transactions in Numia’s data are structured to provide all the necessary details for analyzing user activity and blockchain operations.
Messages
Messages (Msgs) are the core actions within a transaction, designed to trigger state transitions. A single transaction may include one or more messages. For example:
- A
MsgSendmessage transfers tokens. - A
MsgDelegatemessage stakes tokens with a validator.
Messages define the intent behind each transaction and are critical for understanding the purpose of blockchain activity.
Events and attributes
Events provide granular details about actions triggered by transactions. These attributes allow for precise filtering and analysis of events, offering deep insights into blockchain activity. Each event includes:
- Type: A high-level category for filtering events (e.g.,
messagefor actions related toMsgs). - Attributes: Key-value pairs that describe the event in detail, such as:
message.action={some_action}message.module={some_module}message.sender={some_sender}
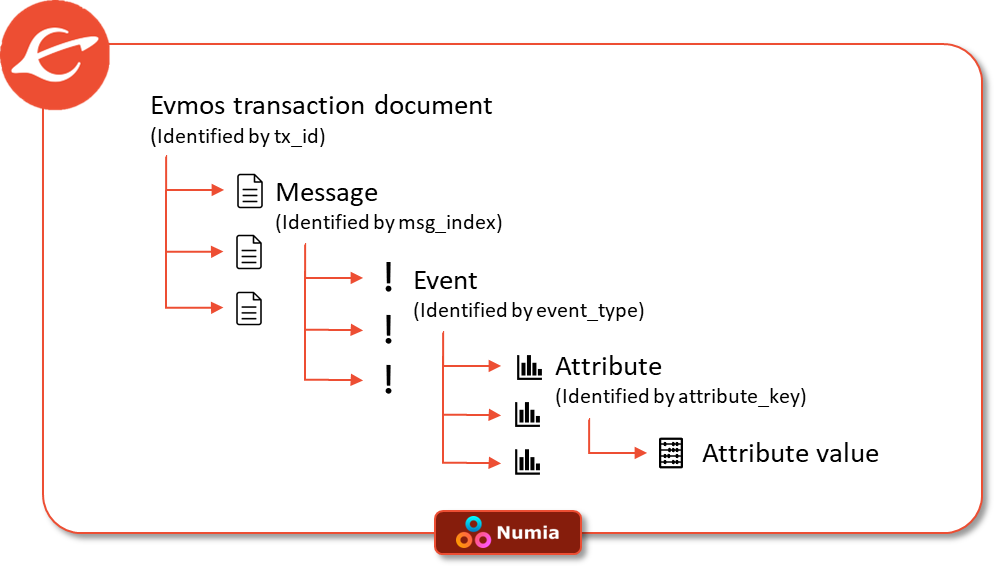
Standardized data across chains
Numia’s datasets are based on the standardized Cosmos SDK data model, making it easy to analyze multiple chains like Evmos, Osmosis, and other Cosmos-based networks. Every chain in Numia’s dataset includes:
Base Raw Tables
These foundational tables follow the Cosmos SDK structure.
Expanded Views
Built on the raw tables, these views simplify data analysis for each chain.
Start with simple queries on each table to understand the data structure. Compare Numia’s data with blockchain explorers like Mintscan to familiarize yourself with how the raw data aligns with the Cosmos SDK schema.